Couchbase
Overview
Couchbase is a NoSQL database which provides an SQL-like querying interaction. For details, see https://couchbase.com. Couchbase provides a set of example databases (buckets) including “beer-sample” and “travel-sample” ones. See the following for more information https://docs.couchbase.com/server/current/manage/manage-settings/install-sample-buckets.html.
Qarbine can natively query Couchbase and obtain deeply nested records such as shown below.
. . .
Qarbine can easily analyze this deeply nested data and format an analysis report. This interaction can also be embedded into applications for a seamless end user experience. Sample output is shown below.
The left hand geomap drop pin can be clicked to open Google Maps at the location. The address listing is not shown above but can be formatted in a variety of manners. This report result can then be exported into various popular formats and easily shared within leading collaboration tools.
Example Qarbine Data Sources
Qarbine supports Couchbase queries enabled by the underlying Couchbase Node.js driver. In general this means any SQL++ (N1QL) query along with any data structures that may be returned.
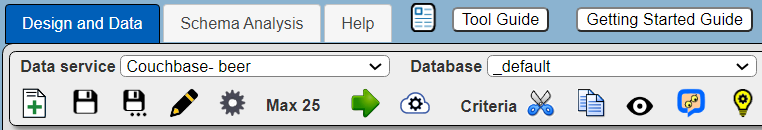
Shown below is the Data Source Designer using a Couchbase data service and accessing the sample Couchbase beer content.
A sample query specification is shown below.
The data service references the following Couchbase Capella data.

Some of the query results are shown below
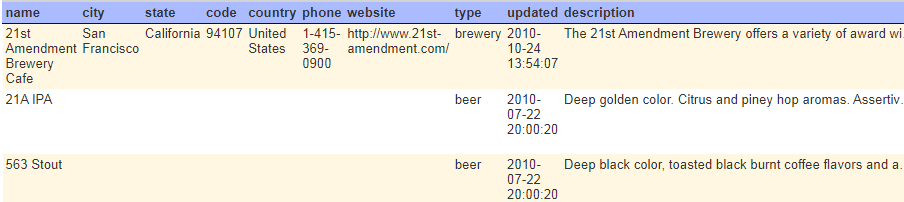
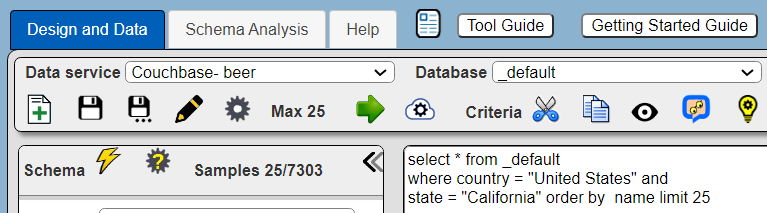
Here is a query with a WHERE clause.
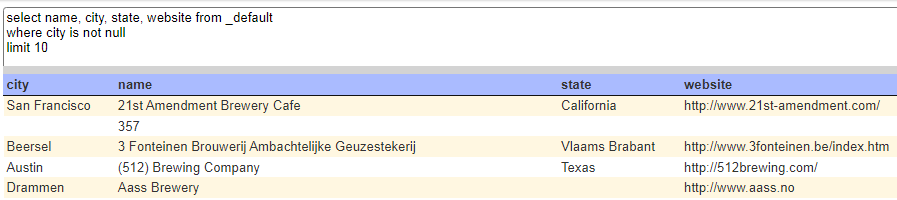
Here is a query with a more involved WHERE clause.
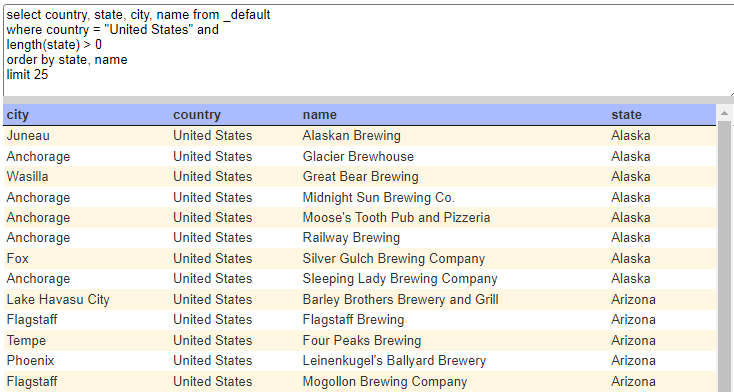
The Couchbase sample travel data has more explicit scopes and collection names as shown below.
A corresponding query specification is shown below.
// If the data service's database is empty then you must explicitly have bucket and scope.
select name,title,country,url,description , address, city, state, geo, reviews
from `travel-sample`.inventory.hotel where country = 'United States'
order by name asc limit 25
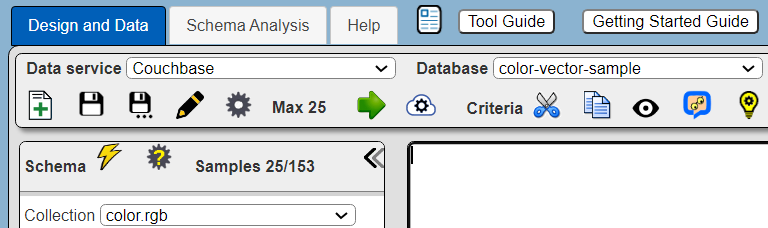
In the Data Source Designer, QBE, and RBE tools, the “Collection” drop down shows names using “scope.collection” format. An example is shown below.
Defining a Data Source
Overview
A Data Source is a Qarbine component responsible for retrieving data from somewhere. At a high level it has a name, a description and some arbitrary query string which when sent to the associated Qarbine Data Service endpoint returns some data. The overall execution flow for an analysis, including the optional prompt component, is shown below.
A single data source can be referenced by name from multiple Qarbine template components. This enables a single point of change when perhaps, an index is added, or some other query tweak is necessary. The alternative is to attempt to find all templates impacted by a schema or index change for example. The component reusability is especially beneficial when team members have varying roles and skills.
Example
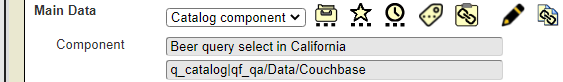
The data source below retrieves beer offerings in California.
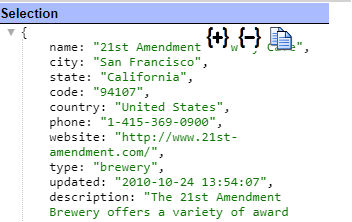
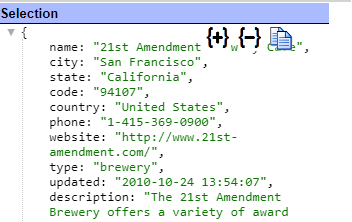
A sample result element is shown below.
The details of that element are shown below
. . .
When the Qarbine data service’s database field is empty, you will have to fully qualify the collection path in your queries with Bucket.Scope.Collection. If there are dashes in any of the pieces then use tick marks to enclose the string. For example, `travel-sample`.inventory.hotel.
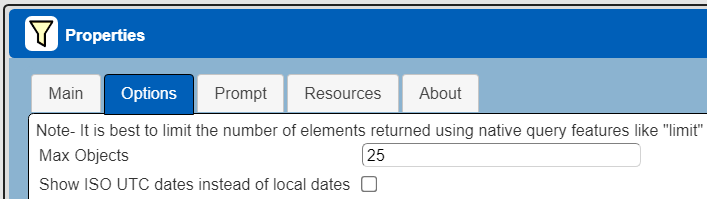
Managing Answer Set Size
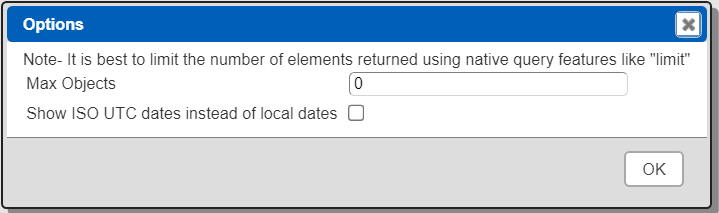
The default maximum number of rows starts off at 25 for a new data source. This is useful to evolve a query from a concept to one that you have verified returns the desired answer set. As noted, any native way of limiting an answer set size is the preferred approach. This setting is in the component dialog as shown below and also accessible by clicking the ‘Gear’ icon.
Once you are done drafting you can adjust this parameter. A “0” indicates there is no maximum. A number greater than 0 indicates to limit the final answer set size to that number of rows. This answer set truncation comes after any native query limit. So, if the answer set from the data endpoint is quite large, that content has to be returned to the Qarbine host. It then may truncate the number of rows. It is best to truncate at the query level (i.e., use a limit) to reduce the content sent from the data endpoint to the Qarbine host in the first place.
Adjusting the Maximum Rows
Recall the default maximum rows at the component level is 25. When you are satisfied with your query you can change that setting by clicking.
Adjust the setting to “0” indicating no Qarbine answer set truncation.
Click
Saving the Data Source
To save the data source click
Navigate to the catalog folder of interest.
In the Catalog dialog, fill in the name, description and other fields.
Click
The data source is saved in the catalog and is remembered as a recent data source as well.
Defining an Analysis Template
Overview
A template defines how to process the data being retrieved from Data Source queries and other data expressions. It also defines formulas, formatting options, and other analysis and presentation options. Team members can define templates which can be easily discovered by others for their running or to use as a starting point for other templates. The overall execution flow for an analysis, including the optional prompt component, is shown below
Example
The Data Source above is referenced in the main properties of the template.
. . .
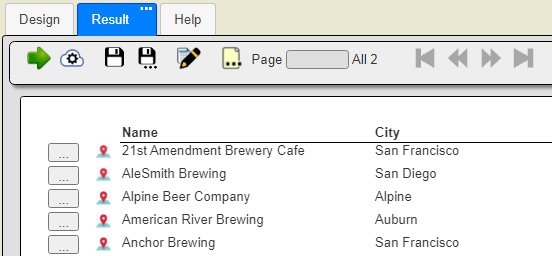
The template includes group header labels for the Name and the City.
The body of the template displays each beer’s name and city.
To their left there is a Callout custom cell button to get the description of the beer location. The “pt” cell formula is
It creates the “pt” variable with the label, latitude, and longitude values. This variable is referenced by the custom map cell as described below. The “pt” cell result is not displayed so it is suppressed via
The cell is a custom Google Map cell that when clicked opens another tab using maps.google.com web site on the given location.
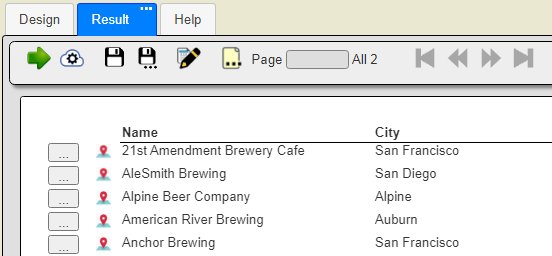
Running the template results in the text oriented information shown below
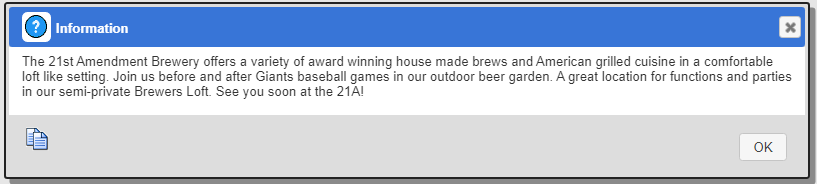
Clicking the left hand icon on the output body lines shows
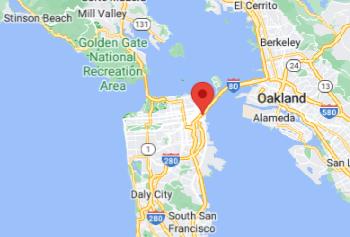
Clicking icon shows a Google Map for the geographic location in another tab.
Saving the Template
To save the template click
Navigate to the catalog folder of interest.
In the Catalog dialog, fill in the name, description and other fields.
Click
The data source is saved in the catalog and is remembered as a recent template as well.
Adding a Map to the Analysis
A custom cell supporting embedded maps may be available depending on the Qarbine edition and release level. This custom cell can be placed on the group summary to render a map of the collected locations. In this case the group summary contains the custom map cell as shown below.
Its formula is
On the right hand side the custom properties include
While processing the body the beer locations are added to the marker list via
That list is used to populate a map in the result with a marker for each beer location.
Sample output from this custom cell is shown below.
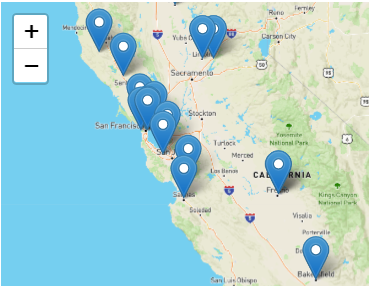
Saving the Updated Template
To save the updated template click
Since the component is already in the catalog no Catalog dialog prompt is presented. The template is updated in the catalog and is remembered as a recent data source as well.
Usage Notes
Result Element Adjustments
For the query “select * from `bucket` “ the Couchbase server returns a list of elements to the Qarbine driver which are objects with a field ‘Document’.
[
{Document: { field1: value1, field2, value2} }
. . .
]
In this case to provide much simpler answer set access, the Qarbine driver preprocesses the elements and returns the final results as
[
{field1: value1, field2, value2}
. . .
]
Query Preprocessing
When the data service is configured by the Qarbine administrator with a bucket, then for the query
select * from collection …
the Qarbine driver will preprocess the query so that the effective query sent to the Couchbase server is
select *from `bucket`._collection …
Analytics vs Standard Queries
To indicate that a Couchbase analytics query is to be used, prefix the query with “analytics “. The internal difference is the use of cluster.analyticsQuery() vs. cluster.query(...). A discussion of the differences can be found at
Color Vector Searching
The following vector search example is based on the information at
It has a very minimal embedding dimension size. Below is an example data source query
#pragma pullFieldsUp rgb
#pragma deleteFields colorvect_l2, embedding_vector_dot
SELECT *, meta().id
FROM rgbBucket.rgbScope.rgb
where
SEARCH( rgbScope.rgb,
{
"fields": ["*"],
"query": {
"min": 70,
"max": 80,
"inclusive_min": false,
"inclusive_max": true,
"field": "brightness"
},
"knn": [
{
"k": 1,
"field": "embedding_vector_dot",
"vector": [! embeddings(@prompt) !]
}
]
}
)
limit 5
This example can be found in the Qarbine catalog as “/example/Couchbase/Colors with vector search large”.
This query uses the “[! macro expression !]” placeholder syntax and references the @prompt variable. That value is obtained using a prompt as shown below.
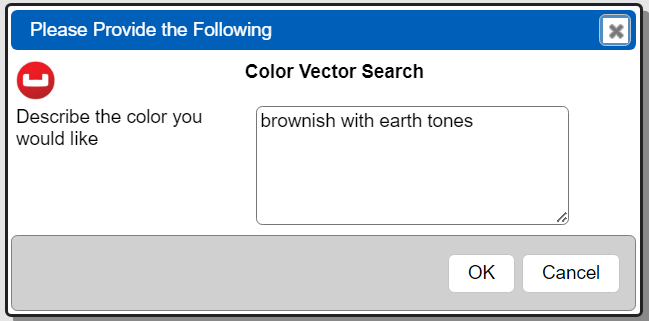
The Prompt has these elements

This example can be found in the Qarbine catalog as “/example/Couchbase/Prompt for color search”.
Travel-Sample Searching
Air Travel Related Schema
Another installable sample Couchbase dataset is the travel-sample. The schema for the travel-sample content is below from https://github.com/couchbase-examples/nodejs-quickstart.
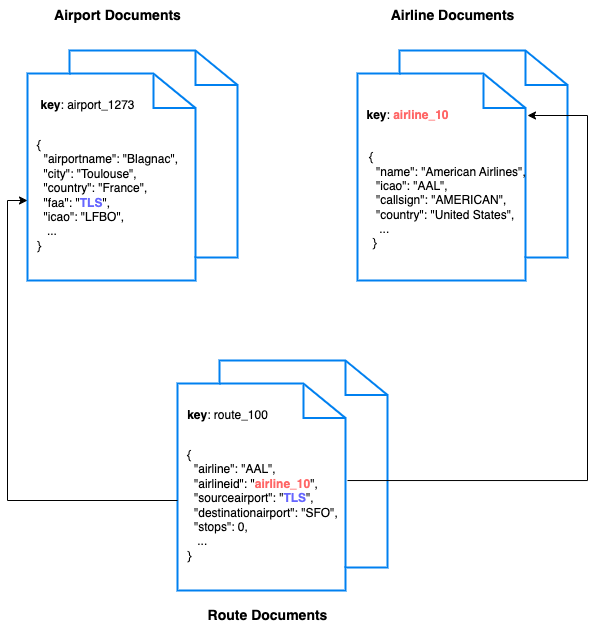
Hotel Collection
The hotel collection of the travel-sample data contains many fields including a description field. An additional field containing the embedding value of the description can be added to each row. In our example the field is named “description_em”. This can be done by querying for the id and description, obtaining the embedding for the description, and then upserting the document with that new embedding field.
Next, a vector search index is created on that field. It is named “description_v2” in our example and is available for semantic searching.
A sample data source query is shown below.
#pragma deleteFields description_em
select *
FROM `travel-sample`.inventory.hotel
where SEARCH( inventory.description_v2,
{
"fields": ["*"],
"query": {
"match_none": ""
},
"knn": [
{
"k": 5,
"field": "description_em",
"vector": [! embeddings(@prompt, 'myOpenAI') !]
}
]
}
)
The #pragma line is used because we used “SELECT *” and really do not need to have the 1536 floating point numbers of the embedding column returned as part of the answer set. The “k” value of 5 is effectively a “LIMIT 5” in the SQL sense.
This data source references a prompt which is shown below.
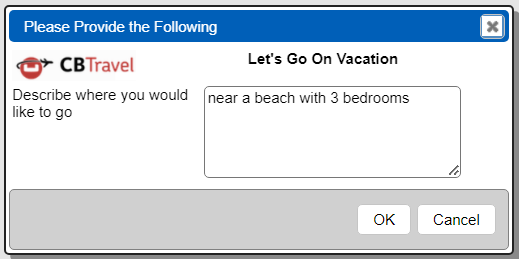
It sets the variable named “prompt” which is used by the following query line
"vector": [! embeddings(@prompt, 'myOpenAI') !]
The phrase the user enters is sent to the Qarbine configured AI Assistant with the alias of “myOpenAI” to obtain a vector search embedding. That value is used in the final query sent to Couchbase. The answer set is retrieved and passed along the template execution pathway. That and the template definition are used to format the analysis.
Remember that the model used to populate the Couchbase collection columns (description_em) must be the same one used to retrieve the embedding for the query.
The sample data source is located at
example/Couchbase/Travel vector search with user prompt
It references the prompt at
example/Couchbase/Prompt for travel search
A template using this combination is at
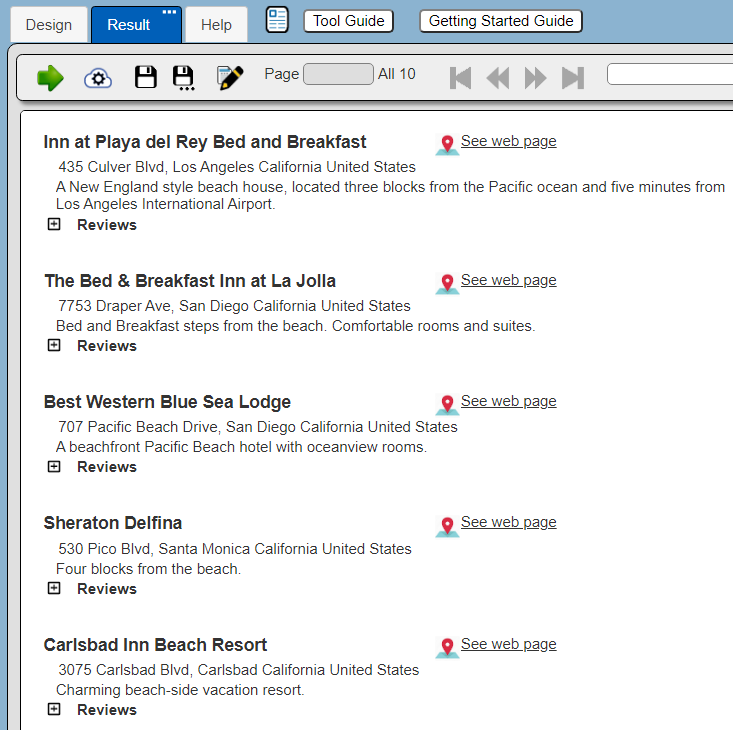
example/Couchbase/hotels and description with vector search
It uses the HTML Toggle Group custom cell to collapse and show the reviews. Below is an example result with the review groups all collapsed via control-alt-clicking on a [-].
Next Steps
Accessing Your Database
For Qarbine Administrators, to configure access to Couchbase see the guides at
http://doc.qarbine.com/docs/category/data-service-configuration
Querying Your Database
For database specific interaction guides navigate to
http://doc.qarbine.com/docs/category/data-source-designer